New gTLD domains top 500,000 as Schilling goes on parking spree
The total number of new gTLD domains broke through half a million for the first time yesterday, but it seems to be due to Frank Schilling obtaining tens of thousands of names in his own TLDs.
Uniregistry’s .link became the fifth-largest new gTLD, moving almost 20,000 names, but it appears that the vast majority are registered to a company affiliated with CEO Schilling.
Uniregistry’s other gTLDs — .tattoo, .sexy, .pics, .photo and .gift — all saw huge jumps too, apparently for the same reason.
This morning’s .link zone files show a pop of 19,945 names, to a total of 20,050.
That would be the third-best GA-day performance, after .guru and .berlin, of any new gTLD to date, but it seems the vast majority are actually premium names acquired by a Uniregistry affiliate.
Of those new .link names, 18,272 (91%) are being parked on internettraffic.com, another Schilling company.
I took a random sampling and found them all registered to North Sound Names, a company based on Seven Mile Beach in Grand Cayman, which is where Schilling lives.
Schilling said this on Twitter yesterday:
@TimJamesDomains @DomainNameWire .. they are the company that has done a deal for our premium names
— Frank Schilling (@Frank_Schilling) April 15, 2014
Premium names are of course those that were reserved by the registry. So either a third-party has bought them wholesale, or Uniregistry has simply shifted them over to an affiliated company.
I’ve asked Schilling to confirm that North Sound Names is also his company and will update this post with his answer.
Testing some domains in Uniregistry’s other gTLDs, I found a similar pattern — big spike, mostly parked at internettraffic.com, North Sound Names in a sampling of the Whois.
Here’s a screenshot of today’s best-performing new gTLDs from DI PRO (click to enlarge):
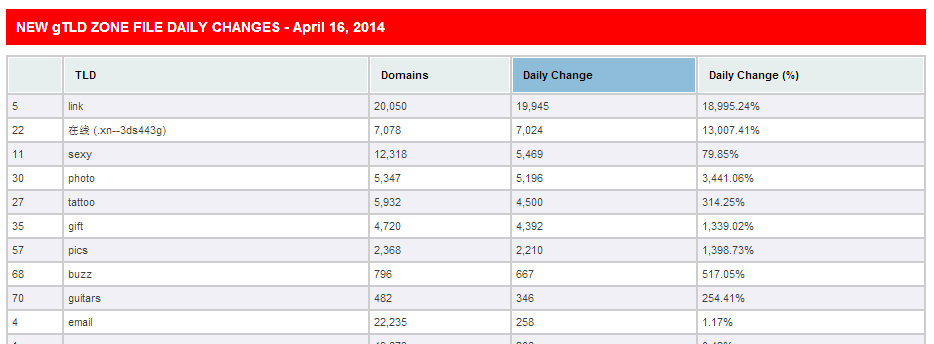
Overall, six of Uniregistry’s new gTLDs grew by a total of 50,735 domains today — 95% of the 53,147 industry total — and internettraffic.com’s name servers are responsible for 37,668 new names.
This brings the total number of “registered” domains to 538,093, though I would suggest that this metric may no longer be a decent measurement of actual end user interest in new gTLD domains.
Pricey .luxury made $500k already
The new gTLD .luxury seems to have sold more than $500,000 worth of domain names already.
(UPDATE: That’s probably not accurate. I seem to have misread some registrar pricing pages. The sunrise price was actually much lower than $1,000. See comments below.)
Saturday’s zone file for the Luxury Partners-owned TLD popped from 1 domain to 470 domains. Most of the new names appear to have been registered during the sunrise period, which ended early last week.
Given the current retail price of over $1,000, it seems .luxury is already a $500,000 business, at least for 2014. Renewal pricing is around the $700 mark, equating to $329,000 a year just on sunrise registrations.
That’s including the registrar markup, of course. The registry will be making a bit less.
“Luxury” brands such as Cartier and Formula 1 bought multiple domains during sunrise. Some tech firms, such as Facebook and Google, continued their blanket approach to defensives.
With such a high price, one wonders what some of these rights holders are thinking: do they really believe cybersquatters are prepared to drop $700 a year infringing their brands?
Sadly there are already a couple of examples of newbie squatters spending absurd sums on clearly infringing new gTLD domains.
It will be interesting to see whether any of these registrants actually use their domains, or whether they’re mainly defensive registrations. I suspect the latter will be more often the case.
Currently in landrush, .luxury is due to go to general availability in about a month.
Belgium comes out against Donuts’ .spa bid
Belgium wants Donuts’ application for .spa rejected after the new gTLD applicant declined to sign a deal with the city of Spa.
In a March 20 letter to ICANN, published today, the Belgian deputy prime minister Johan Vande Lanotte said “negotiations between the stakeholders are closed”, adding that Belgium:
requests the Board of Directors of the ICANN to delegate the new “.spa” gTLD to the candidate who has a formal agreement with the local authorities of Spa and in respect of the public interest.
That’s the other applicant in the two-horse .spa race, Asia Spa and Wellness Promotion Council, which has promised to earmark up to 25% of its European profits to spa-related uses in the environs of Spa.
The letter was sent a week before the Governmental Advisory Committee issued its Singapore communique, which noncommittally noted that it “welcomes” the agreement between Spa and ASWPC.
ICANN may or may not be currently in receipt of firm, consensus GAC advice to accept or reject either of the remaining .spa applications.
In Beijing a year ago, the GAC put .spa on a list of gTLD strings where “further GAC consideration may be warranted” and asked ICANN to “not proceed beyond Initial Evaluation”.
At the Durban and Buenos Aires meetings last year the GAC said ICANN should not “proceed beyond initial evaluation until the agreements between the relevant parties are reached.”
Given that Donuts and Spa evidently cannot come to an agreement, ICANN presumably remains advised to keep one or both .spa applications on hold. The advice is pretty vague.
The string “spa” is not a geographic name within the rules of the new gTLD program. Donuts argues that it’s too generic nowadays to belong just to Spa.
Geo gTLDs catch a break with new launch rules
New gTLDs with a geographic or community focus have won concessions from ICANN under new rules published today.
All new gTLD registries will be able to allocate names to public authorities, matching for example district names or landmarks, even if those names match trademarks in the Trademark Clearinghouse.
The change came in the final version of the Qualified Launch Program guidelines, which spells out how new registries are able to allocate up to 100 names, pre-sunrise, to anchor tenants.
The new language related to public authorities reads says that any registry, may give names to any “international, national, regional, local or municipal governmental authority”.
Such domains must match “the name of a building, park, monument, airport or other public place… region, city, street, district or other geographic area” operated by the authority, the name or acronym of the authority itself, or the name of one of its public services.
The carve-out would allow (to use a Minds + Machines example), the .london registry to give thepolice.london to the Metropolitan Police, even if the Sting-fronted band The Police had a matching mark in the TMCH.
The newly amended rules apply to all new gTLDs, not only those that were classified as “geographic” under ICANN’s rules. So they would apply to .scot, for example, even though it’s not strictly a geographic name.
But the QLP still would prevent registries allocating a TMCH-listed string to anyone prior to their sunrise period concluding, unless the entity getting the name also owned the TMCH listing.
The new QLP rules are available here.
Famous Four wins .party gTLD contest
Famous Four Media has won the .party new gTLD contention set after coming to a private agreement with the only other applicant for the string, Oriental Trading Company.
Financial details of the arrangement were not disclosed.
Oriental Trading is a supplier of party goods that intended to run the gTLD as closed, single-registrant namespace.
But Famous Four expects the open .party registry to be used for parties in the social gathering and political senses of the word.
It now has 13 uncontested applications and 44 more outstanding.
In related news, Minds + Machines today announced that it intends to take at least three of its applications — .garden, .property, and .yoga — at a private auction April 22 managed by Applicant Auction.
Republicans advance “embarrassing” DOTCOM Act
Republican US Congressmen today voted to advance the DOTCOM Act, which would add a delay of up to a year to the IANA transition.
The Communications and Technology Subcommittee voted 16 to 10, split directly along party lines, to advance the bill to the next stage of the US legislative process.
The bill (pdf) has been changed since last time I reported on it. For ICANN, the change is for the worse.
It would now block the National Telecommunications and Information Administration from approving ICANN’s proposal for an NTIA-free future for up to one year while the Government Accountability Office prepares an analysis.
In the first draft, that delay would begin at the moment the bill hit the statute books. Now, the clock starts when the proposal is made.
Democrats on the subcommittee, who had four amendments shot down by the Republican majority during a markup session today, said the bill makes a mockery of the multistakeholder process they all profess to endorse.
Ranking member Anna Eshoo noted that Democrats supported a GAO report, but did not want the NTIA’s hands tied.
She reminded her opponents that they had all voted for a bill in 2012 — shortly before the International Telecommunications Union met for its WCIT conference — affirming the United States government’s commitment to multistakeholder management of the internet.
“Today you are unraveling exactly what you voted for,” she said, accusing Republicans of seeing “black helicopters” and a “conspiracy” by President Obama to give the internet to authoritarian regimes.
“It’s a source of embarrassment for a committee that has for the most part operated in a very respectful bipartisan way,” he said.
Republicans in response said that it is not unreasonable to request a GAO report, to help them understand the possible consequences of the IANA transition.
Rep John Shimkus, the primary sponsor of the DOTCOM Act, said that the forced delay was needed to give the bill “teeth”. Without it, he said, the GAO report could come after the IANA transition has already taken place.
In a concurrent hearing elsewhere on Capitol Hill, ICANN CEO Fadi Chehade was busy explaining to a different committee why he could not support the bill.
The DOTCOM Act would give the impression that the US government does not take the multistakeholder model seriously and does not trust ICANN, he said.
While Republicans may feel like the bill will keep the DNS root out of the hands of Russia and China, what they’re actually doing is giving those nations fuel for their power grabs in government-led international fora such as the ITU, in other words.
The DOTCOM Act is not yet law. It still has to go through the full House (Republican-controlled) and Senate (Democrat-controlled) and be signed by President Obama (China-controlled) before it hits the statute books.
ICANN sets ball rolling on IANA transition
ICANN has put the wheels in motion towards the ultimate transition of the IANA functions from the stewardship of the US government.
The organization put forward a proposal this morning, apparently compiled from views gathered at the ICANN 49 meeting in Singapore and mailing list suggestions.
It’s a proposal for a process to develop process to develop a proposal:
Call for Public Input: Draft Proposal, Based on Initial Community Feedback, of the Principles and Mechanisms and the Process to Develop a Proposal to Transition NTIA’s Stewardship of the IANA Functions
Basically, ICANN is proposing that a new “steering group” be formed, tasked with leading the development of a proposal to transition the stewardship of the IANA out of the hands of the US government.
ICANN hopes to have it sitting by the ICANN 50 meeting in London this June, but right now it wants your comments on whether this group should be created, who should be on it, and what it would do.
The idea is that the group would create a process for the community to create the IANA transition proposal.
The proposal itself would be created by the “community” and presumably put into written form by the steering group.
Whatever was agreed upon would be submitted to the US National Telecommunications and Information Administration for approval, probably before the IANA contract expires in September 2015.
It is complicated, but the gist of it is that everyone gets a say and every discussion will be had in the usual glare of ICANN transparency.
Who’s on the committee?
The steering committee would comprise 22 members and an ICANN board liaison.
Two members would be drawn from the each of the following ICANN bodies: GNSO, ccNSO, ASO, ALAC, RSSAC, SSAC, GAC.
Two members would come from each of these external IANA-user bodies: IAB, ISOC, IETF, NRO.
Here’s a friendly ICANN illustration:

For those of you worried about Russia, China, etc, taking over the internet, allow me to state this in layman’s terms: there would only be two government representatives on the panel.
I guess there could be three or four, in the unlikely event that one or both ccNSO representatives comes from a government-run ccTLD. Either way, it’s a small minority of the group.
In terms of pure numbers the geeks would rule the committee, with wonks, lawyers and industry folk making up the remainder.
I can see the GNSO wanting more spots. The domain industry, non-commercial users and IP interests are all in the GNSO and all have divergent views. Two seats, the GNSO might argue, might not be enough.
That said, many members of advisory committees such as the SSAC and RSSAC are firmly from the registry side of the industry, so industry may have a bigger seat a the table.
Which parts of the community get what portion of representation is going to depend on who puts themselves forward and who gets picked to participate.
The committee members would be selected by ICANN chair Steve Crocker and GAC chair Heather Dryden from the pool of people who volunteer.
What would it do?
The steering group, as mentioned, is supposed to guide the community discussions, taking input from everyone. It doesn’t seem to be a working group in the usual ICANN sense, where only members have a voice.
The process of gathering this input would be designed by the committee itself, adhering to principles such as timeliness, outreach and consensus.
Whatever transition proposal was ultimately presented would have to adhere to the NTIA’s guidance on what it’s looking for, which includes the “no intergovernmental solution” rule.
In this diagram, the green bits are the blanks that the community is being asked to fill in.

A good question might be to ask what its job is not, which is answered in a new “scoping document” (pdf) that ICANN published today.
For example, while I wrote an article earlier this week suggesting that the Governmental Advisory Committee needs to have its internal rules put in check before a transition, that would be outside scope. ICANN says:
As NTIA currently plays no unique role in the development of policies for the coordination of the Internet’s domain name system, the proposal is not about how relevant policies are created, nor the relevant structures in which they are created.
The process is not about reforming how ICANN works, in other words, it’s about creating some kind of accountability mechanism to replace the NTIA.
I have no clue what that would look like. Probably a committee or something. More bureaucracy, no doubt.
The fundamental problem, it seems to me, is that the NTIA doesn’t actually do anything. Any true replacement would therefore have to be redundant by design.
The only function the NTIA has actually played over the last 16 years is as a sword of Damocles, a constant threat that if ICANN goes rogue it will lose its IANA contract.
That’s not something that can be replaced, surely? And if the multi-stakeholder process works as well as ICANN claims it does, surely it doesn’t even need to be replaced.
Perhaps I simply lack imagination.
Anyway, because this is a multi-stakeholder process, you (yes, even you!) can read today’s proposal here and submit your comments to the email address provided.
Four governments file ICANN appeals over .wine
France, Spain, the UK and the European Commission have formally appealed ICANN’s decision to allow the .wine and .vin new gTLD applications to proceed.
In doing so, they’ve become the first national governments to file Requests for Reconsideration with ICANN since the process was introduced in 1999.
All four governments are demanding that ICANN take another look at its March 22 resolution in which it said .wine and .vin could be taken off hold and proceed through the remainder of the new gTLD process.
The four applications in question (three for .wine, one for .vin) have been frozen since the Beijing meeting a year ago, at which the Governmental Advisory Committee said it needed more time to consider them.
European nations, with some Latin American support, think that wine-related gTLDs should not be approved unless the applicants agree to give special protection to geographic indicators, such as “Champagne”.
The RfRs are all, as you might expect, a bit “inside baseball”, focusing on the minutiae of ICANN’s bylaws.
What’s illegal and what isn’t?
A key concern is that ICANN’s New gTLD Program Committee, in passing the resolution, relied in part on an analysis of the legal issues (pdf) conducted by French law professor Jerome Passa.
Passa concluded that there’s nothing under the law to prevent ICANN assigning .wine to Donuts, one of the applicants, because “wine” is not a protected GI string.
As regards the applications for the assignment of the new gTLDs ‘.vin’ and ‘.wine’ filed by the Donuts company, there is no rule of the law of geographical indications, nor any general principle which obliges ICANN to reject the applications or accept the applications under certain specific conditions.
From my reading of Passa’s opinion, a domain name containing a GI would only be illegal if it was used to sell counterfeit wines.
For example, it would be perfectly okay for a Chinese registrant to own champagne.wine if he used it to sell genuine champagne from Champagne, but it would be uncool if he used it to sell champagne-style sparkling wine.
Passa doesn’t seem to think it would be necessarily illegal for a registry to sell that domain, or for ICANN to delegate a .wine gTLD that could possibly be abused by said registrant in future.
The four governments are not so much concerned by his legal arguments (though they do disagree with them), but rather by the fact that the GAC was not shown Passa’s opinion before the NGPC made its decision
Under section XI-A of ICANN’s governing bylaws, the GAC “shall have an opportunity to comment upon any external advice received prior to any decision by the Board.”
By not giving Passa’s analysis to the GAC prior to its March 22 resolution, the NGPC violated ICANN’s bylaws, the four governments argue.
However, ICANN has already responded to this argument and others, suggesting that the four new RfRs may already be dead in the water.
In a resolution last Thursday the NGPC stated that the bylaws were not broken because the requirement to show the GAC “external expert advice” only applies when the board is determining matters of policy.
An explanation of last week’s NGPC decision says:
the NGPC has concluded that there was no process violation or procedural error under the Bylaws, particularly because the Independent Legal Analysis was not sought as External Expert Advice pursuant to Article X1-A, or any other Bylaws provision. Rather, the Independent Legal Analysis was sought pursuant to Module 3.1 of the Applicant Guidebook, and partly at the GAC’s suggestion.
Basically, it’s round two the old “policy versus implementation” debate, in which the ICANN board and GNSO Council have regularly sparred, kicking off with new opponents.
Spain argues in its RfR that the bylaws “the supreme governing rules” of ICANN, apply to implementation matters too and that there’s “no legal basis” for ICANN’s finding that they only apply to policy.
It further notes that a legal analysis of the related .amazon new gTLD controversy, also written by Passa, has been circulated to the GAC for comment as per the bylaws.
Disturbing views on “consensus”
In order for an RfR to be successful, complainants have to show that the ICANN board or NGPC did not consider all the evidence they should have at the time of their decision.
The governments are only slippery ground here, as all they can seem to point to are the barrage of letters that have been sent to ICANN by wine producers, associations and governments over the last year or so.
It may not have mentioned each one explicitly in its resolution but it’s very unlikely, in my view, that the NGPC was not aware of these letters when it made its call.
More significantly, these objecting governments are arguing that the NGPC was misled by GAC chair Heather Dryden about the extent of “consensus” in the GAC with regards .wine and .vin.
Dryden told ICANN in a September 9, 2013 letter that the GAC had not reached a consensus to object to the two new gTLDs, so they could proceed.
It appeared that the GAC — with members such as the US, Canada and Australia disagreeing with Europe — had simply hit an immovable brick wall in its talks, so consensus was never going to be reached.
France states in its RfR that the Dryden letter was sent without first consulting the GAC:
The GAC Chair’s statement that “The GAC has finalised its consideration of the strings .wine and .vin and further advises that the applications should proceed through the normal evaluation process” is not a consensus view of the GAC as per the aforementioned Operating Principle, but a mere interpretation and opinion of the GAC Chair.
Where France’s opinion, which seems to match previous statements by the European Commission, gets disturbing is in its interpretation of what “consensus” means. It wrote:
in reality a significant number of GAC members were in consensus not to allow the .WINE and .VIN applications to proceed through evaluation until sufficient additional safeguards were in place. The reality is that the GAC as a whole could not reach consensus, what does not necessarily imply that the strings can proceed through the normal evaluation process without further consideration.
It’s worded awkwardly, but France seems to be saying that agreement among a certain subset of GAC members (ie, the Europeans) somehow constitutes a GAC consensus that the applications should be indefinitely delayed.
It’s disturbing close to arguing for majority rule on the GAC, which as I explained in depth earlier this week is something to be avoided at all costs.
Anyway, that’s the second prong of the RfR attack: whether the NGPC had been misled about the GAC’s views.
The four separate RfRs appeared on the ICANN web site today. The file labeled as being from the European Commission appears to be a copy of the French one; possibly an uploading error.
UPDATE: It was an uploading error. You can find a copy of the European Commission RfR here (pdf).
How Russia and China could take over the internet!
Do governments have too much potential power over ICANN, and do they need reining in before the US cuts itself loose?
It’s a question that’s emerging given the recent decision of the United States government to remove itself from stewardship of the domain name system root zone.
The US National Telecommunications and Information Administration may have no intention of allowing other governments to replace it as overseer of the IANA functions, but that doesn’t mean that governments won’t be able to abuse their powers in future under ICANN’s existing structures.
Before getting into the arguments, I should first apologize for the misleading, clickbaiting headline on this post. It’s a sarcastic response to the misleading narrative that has been set by much of the mainstream media in the US.
For the record, I don’t think Russia and China are going to take over the internet, ICANN or the DNS.
What I’d like to look at here are ways in which the Governmental Advisory Committee might need to be reformed in order to maintain balance and prevent capture by any bad government in future.
And by “bad government”, I’m not just talking about Russia, China, Iran and any other boogeyman that may pop up in future; I could just as easily mean the United States and European Union member states.
I’m basing quite a lot of this on concerns raised by NetChoice Coalition’s Steve DelBianco in a Congressional hearing last week.
While DelBianco seems to be generally pro-transition, he outlined several “stress test” scenarios that he believes need to be addressed during the stewardship transition process.
Among other things, DelBianco said: “It will be important for the transition plan to prevent any government-led organization from replacing the former U.S. role after the transition is complete.”
Everyone, from the lunatic fringe of the US media that bases its reporting on GOP talking points to the senior management of ICANN and the NTIA itself, is on the same page here.
Nobody wants the US to be replaced by an intergovernmental alternative.
Indeed, baked into the NTIA’s proposal to relinquish its stewardship powers is an explicit promise that a government-led replacement will not be approved. It ain’t going to happen.
But governments already have a powerful voice within ICANN, in the form of the Governmental Advisory Committee.
The GAC
While all national governments are welcome at the GAC, it currently has around 130-odd listed members.
Typically, fewer than half actually show up to in-person ICANN meetings. DelBianco reports that there were 61 in attendance at the ICANN 49 meeting in Singapore two weeks ago.
The GAC has the ability to issue “advice” to the ICANN board of directors.
The board is free to accept or reject this advice. Rejection, which can and does happen, triggers a lengthy consultation process in which both parties attempt to reconcile their differences.
In practice, ICANN tends to bend over backwards to accommodate GAC advice, even to the point of occasionally willfully misinterpreting it in order to make it appear that it has been accepted.
Under Principle 47 of the current GAC Operating Principles it would be virtually impossible for a government or group of governments to capture the GAC. The GAC only issues advice by consensus:
The GAC works on the basis of seeking consensus among its membership. Consistent with United Nations practice, consensus is understood to mean the practice of adopting decisions by general agreement in the absence of any formal objection. Where consensus is not possible, the Chair shall convey the full range of views expressed by members to the ICANN Board.
If China and Russia managed to persuade every other GAC member to agree with a repressive policy they wanted to introduce, the United States could hold out and destroy consensus.
And, it should be said, vice versa.
How the GAC has used its power
The GAC has a track record of issuing advice, by consensus, that trickles down, via ICANN’s contracts with registrars and registries, to affect domain registrants and regular internet users.
Sometimes, the impact could be said to impact human rights issues such as free expression and privacy.
For example, when law enforcement agencies (LEA) such as the FBI and Interpol recommended that registrars should start logging their customers’ IP addresses and should suspend the domains of registrants whose contact information could not be verified, the GAC reissued those recommendations as “GAC/LEA” advice that ICANN eventually accepted.
One could argue that this has free speech and privacy implications, but it came via the consensus of a GAC that included nations with privacy rights enshrined in their constitutions and statute books.
In fact, the United States was one of the strongest advocates for the LEA recommendations becoming part of the registrar contract, as this report from the October 2011 ICANN meeting Dakar will illustrate.
Let’s be clear here: legitimate bloggers are having their web sites suspended today, right now, because of what the US did in the GAC.
I’m singling out the US unfairly here just as a counterpoint to the arguments, emerging in DI comments and elsewhere, to the effect that the US is some kind of unshakeable guardian of internet freedom. It ain’t.
In truth, the GAC’s pro-LEA position at first had majority support (pdf) then, after its Operating Principles were amended in 2011 to clarify what “consensus” means, consensus support (pdf).
All governments can be credited/blamed for this situation.
Blocking TLDs
The GAC also has a track record of compelling ICANN, via its advice, to prevent certain top-level domains from entering the DNS root zone.
In the current round of new gTLD applications, two strings have so far been killed off as a direct result of GAC advice and many more at at risk.
Applications for .thai and .gcc were both thrown out by ICANN because the GAC, by consensus, did not disagree with the objections of the Thai government and the Gulf Cooperation Council.
Amazon.com’s application for .amazon is currently on hold because the GAC, again by consensus, thinks that nations such as Brazil and Peru have better rights to the term.
ICANN has still to make a formal decision on applications for .spa, which the GAC has advised (by consensus) be placed “on hold” until Belgium (unilaterally) decides whether to endorse them or not.
Several other applicants have voluntarily withdrawn their applications after receiving GAC consensus objections.
Many more face losing their deposits unless they comply with GAC advice on matters such as registrant credentialing.
If having a TLD delegated to the root zone is a free speech issue, the GAC already has the power to affect it.
What if Russia tries to ban gay?
Let’s take a hypothetical scenario: Russia wants ICANN to force registrars to suspend the domain names of web sites containing content it considers pro-homosexuality.
Today, Russia would have to get a consensus of the GAC to agree with it — that is, no government objections to its proposal — in order for full-fat GAC advice to make its way to the board.
That, clearly, would not happen. Non-homophobic nations in North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia and no doubt parts of Africa would not stand for such a thing.
There would be no shortage of governments eager to block consensus on such an appalling proposal.
Even if the GAC came to a consensus to ban the gays, ICANN’s board of directors would be able to reject the advice by going through the necessary motions.
If by some crazy turn of events the ICANN board accepted the advice, ICANN would still have to get the contractual changes past the registrars themselves, which would prove challenging.
But what if the GAC operated not by consensus but by majority rule?
What if Russia persuaded enough of its allies and client states to show up to an ICANN meeting to raise their hands at the appropriate moment? It could, conceivably swing a vote.
While the GAC does not issue advice by majority today, it would be a relatively simple matter for it to change its Operating Principles so that voting, not consensus, ruled.
In fact, the Operating Principles state that they can be amended by a simple majority. Principle 53 states:
A Member or Members may move, at a meeting, for these Operating Principles to be open to revision. If so moved, the Chair shall call for the movement to be seconded. If so seconded, then the Chair shall call for a vote to support the resolution. The deciding vote may be by ballot, by the raising or cards, or by roll call, and shall constitute a simple majority of the Members who are present at the meeting at which it was moved for these Operating Principles to be revised. If so resolved in favour of a revision of these Operating Principles, then the proposal shall sit for consultation for a period of sixty (60) days. At the next meeting following the sixty days, the Chair shall call for a vote for or against the proposal. The deciding vote may be taken by ballot, by the raising or cards, or by roll call, and shall be a simple majority of the Members who are present at the meeting at which the vote takes place.
This, the GAC’s current ability to radically change its voting procedures, is at the heart of some of DelBianco’s “stress tests”.
His example below concerns post-delegation censorship of the root itself, rather than individual web sites, but the same rules outlined above apply.
In his testimony (pdf) to Congress, DelBianco said:
a majority of governments in the GAC might advise ICANN to suspend a TLD that refuses to remove domains with content critical of governments (e.g., .corrupt ). Today, this kind of censorship routinely occurs at the edge of the Internet when governments block domestic access to websites, such as Turkey now blocking Twitter. But this scenario envisions censorship moving from the edge to the core of the internet – the root table of TLDs used by the entire world. It’s a critical stress test to examine how the new IANA mechanism could respond if a future ICANN board bowed to GAC advice for censorship at the root of the Internet.
DelBianco is not suggesting that the current ICANN board would cower over a matter of GAC censorship, but we’ve got no idea what the board is going to look like five, 10 or 20 years from now.
If the safeguard of US stewardship is going away, ICANN’s internal processes need to be tough enough to withstand a GAC that goes rogue and starts demanding things that further infringe liberties.
Does ICANN see a problem?
At a press conference during the Singapore meeting two weeks ago, I asked ICANN chair Steve Crocker and CEO Fadi Chehade if the GAC needed to be be reined in to prevent future abuse.
Crocker responded. I’m quoting my question (which wasn’t as detailed as to include references to GAC Operating Principles) so you know exactly what he’s replying to:
DI: This is about the IANA transition process. I was just wondering: the NTIA says they will not accept a multilateral or intergovernmental solution to this transition process, so does it not follow that there should be some safeguards to prevent the GAC becoming too powerful and stopping it becoming a mini-ITU within ICANN? Is that envisaged as part of this process, to put some kind of restraint on the GAC’s power?
CROCKER: As I said in my remarks this morning, the fact that the end result should not be multilateral or intergovernmental certainly did not mean that governments should not be involved. Governments have to be involved. You’ve asked about what happens if the GAC becomes too powerful.
A big problem is getting more involvement of the GAC. We’re still in the process where the GAC is a maturing organization that’s come a long way and is making ever more contributions and we’re some distance away from being worried about whether the GAC is going to take over or become all too powerful.
The way ICANN is structured is very thoroughly multistakeholder and there are a lot of checks of balances built in so that no single constituency has the ability to become dominant or to take over. I think there would be very strong reactions if that ever started to come into play. So I don’t view it as a imminent concern.
We value and encourage the involvement of governments and we understand that for many many governments it’s a novel experience to participate in an environment in which they’re not the only ones speaking.
In short, he’s saying ICANN needs more government participation via the GAC, albeit carefully counterbalanced within the multi-stakeholder environment.
With that in mind, isn’t it fair to ask whether reforms to the GAC’s Operating Principles are a necessary component of the IANA stewardship transition process?
If ICANN is going independent, its structures need to be robust enough for the long term. Maybe that needs to mean a GAC permanently handcuffed to principles of consensus, to prevent capture.
Euro winemakers talk .wine boycott, EU block
European wineries are threatening to boycott .wine and .vin and may lobby for the two new gTLDs to be “blocked” in the EU.
The news follows ICANN’s decision to allow .wine and .vin applications to proceed over the objections of the EU, and its decision a few days later to put both strings on hold for 60 days.
The European Federation of Origin Wines said it was “sceptical” about the 60-day freeze, which was designed to give those who want protection for “geographic indicators” a chance for more talks with applicants.
The EFOW represents geographic indicator interests in France, Italy, Hungary, Portugal and Spain. It said in a press release:
EFOW announces that it envisages “appealing against ICANN’s two successive decisions”. The federation also recalls it “threatens to organise a boycott if the decision to delegate is taken without according GI protection. Moreover, it will also ask for the blocking of these sites in the EU”.
While “asking” is not “getting”, a EU-wide block on a top-level domain would certainly be unprecedented — exactly the kind of Balkanization of the DNS that every rational government strives to avoid.
I doubt the EU would go for it, in other words.
But EU bodies are fighting tooth and nail to get the GI protections that many of their winemakers are asking for.
The European Commission tried to frame the the .wine controversy as a test of the “multistakeholder” process in a press release Friday:
The new gTLDs “.wine” and “.vin” cannot be opened until the rights and interests of wine producers and consumers worldwide are duly protected. If ICANN wants to demonstrate that the multi-stakeholder approach to Internet Governance can work for all, its decisions have to protect the common good and not simply favour purely commercial decisions or the highest bidders.
The alternative argument would be that to bow to the demands of certain governments where the Governmental Advisory Committee cannot find consensus would be to make a mockery of the ICANN process.
The United States, Canada and Australia are among those disagreeing about the need for GI protections, making a GAC consensus impossible. Where the GAC does not have a consensus, ICANN does not have mandate to act.
Let’s not kid ourselves here: every government with an opinion here is just looking out for the commercial interests of its local businesses, so they’re all just as bad as each other in that regard.







Recent Comments